The difference between hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl cellulose
Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC)
Application description:
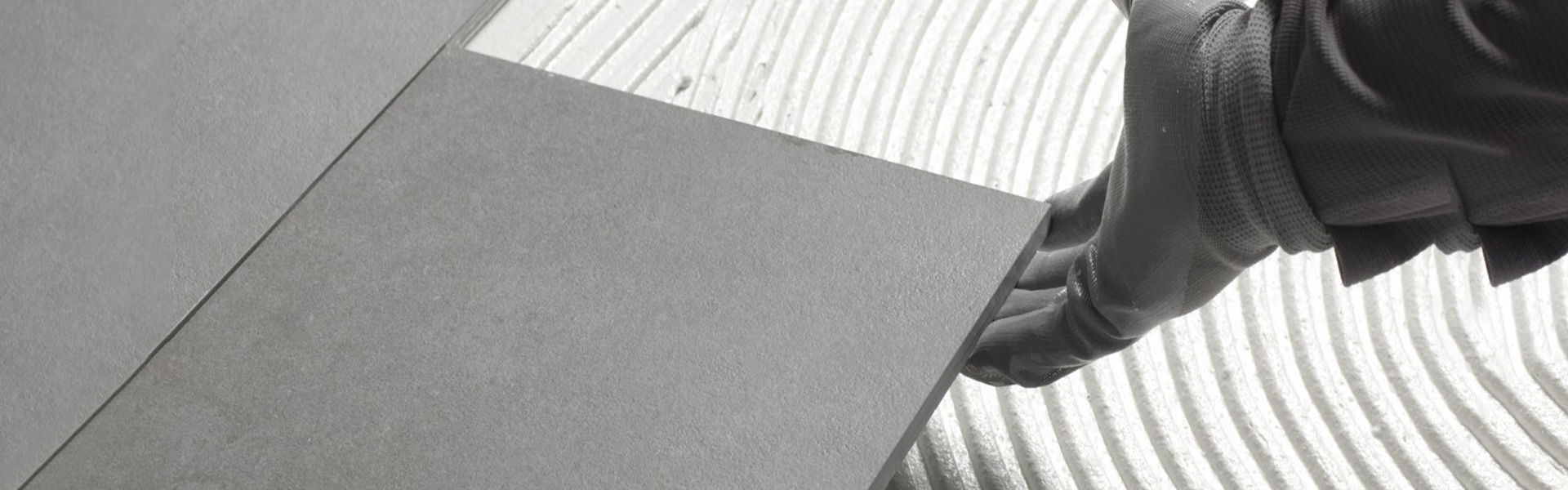
1. Construction industry: as a water-retaining agent and a retarder of water and sediment slurry, the slurry has pumping property.Use mortar, plaster, putty powder or other building materials as a binder to improve applicability and extend operating time.Use as stickup ceramic tile, marble, plastic adornment, stickup aggrandizement, still can reduce cement dosage.HPMC water retention performance makes the paste in the application will not dry too quickly and crack, enhance the strength of hardening.
2. Ceramic manufacturing industry: widely used as adhesives in the manufacture of ceramic products.
3, coating industry: in the coating industry as a thickener, dispersant and stabilizer, in water or organic solvents have a good solubility.As a paint remover.
4, ink printing: in the ink industry as a thickener, dispersant and stabilizer, in water or organic solvents have a good solubility.
5, plastic: forming agent, softener, lubricant, etc.
6, PVC: PVC production as a dispersant, is the main suspension polymerization preparation of PVC additives.
7. Others: this product is also widely used in leather, paper products, fruit and vegetable preservation and textile industry
Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)
As a non-ionic surfactant, hydroxyethyl cellulose has the following properties besides thickening, suspension, adhesion, floatation, film formation, dispersion, water retention and protective colloid:
1. HEC is soluble in hot or cold water, high temperature or boiling without precipitation, giving it a wide range of solubility and viscosity characteristics, and non-thermal gelation;
2. Its non-ionic type can coexist with other water-soluble polymers, surfactants and salts in a large range. It is an excellent colloidal thickener with high concentration of electrolyte solution.
3. Water retention capacity is twice higher than that of methyl cellulose, with good flow regulation.
4. The dispersing ability of HEC is the worst compared with the recognized methyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, but the protective colloid is the strongest.
Usage: generally used as thickening agent, protective agent, adhesive, stabilizer and additive in preparation of emulsion, jelly, ointment, lotion, eye cleaner, suppository and tablet, also used as hydrophilic gel, skeleton material, preparation of skeleton type slow-release preparation, also used as stabilizer in food.
www.hpmccelluloseether.com
Main Category
Popular Articles
- HPMC also known as Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose
- what is Redispersible emulsion powder?
- The difference between hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and hydroxyethyl cellulose
- HPMC Cellulose Ether for Construction Industry
- HPMC for gypsum plaster
- Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose(HPMC)
- top hpmc cellulose ether factory in china
- Which properties of mortar can be improved by redispersible latex powder
Tags
Contact Us
Address:Chemical Industrial Development Zone Jinzhou Hebei,China.
Email:sales@hpmccelluloseether.com
Site: www.hpmccelluloseether.com
Phone:



 Whatsapp
Whatsapp